|
Download Adobe Reader
 Resize font: Resize font:
Azathioprine
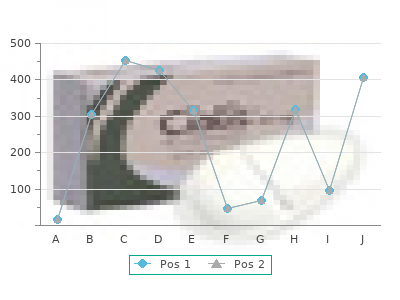
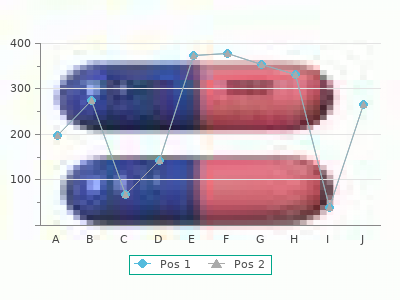
By M. Marus. University of the Sciences in Philadelphia. 2018. Increasing the dose or shortening the dosing interval can only be entertained when the antibiotic being used has a favorable therapeutic ratio buy discount azathioprine 50mg. The rate of clearance of the drug and the Vd are dynamic processes quality 50 mg azathioprine, and very high concentrations of the antibiotic can be the result when dosing is increased in a patient with rapidly resolving pathophysiological hemody- namics of the systemic inflammatory response. Continuous Antibiotic Infusion Antibiotic infusions are commonly given as 30 to 60 minute infusions. This results in the rapid spike in antibiotic concentration in serum that is identified in Figure 1. A very large amount of Antibiotic Kinetics in the Multiple-System Trauma Patient 531 Figure 3 Illustrates the enhanced serum concentration of antibiotics that are achieved when the dose is doubled of a hypothetical drug with a normal dosing interval of six hours and a T1/2 of 1. Figure 4 Illustrates the effects of con- tinuous infusion and prolonged infusion upon the serum concentrations of the theoretical antibiotic model. Continuous infusion is begun after the initial inter- mittent full dose has been administered. The pro- longed infusion results in an area under the curve that is similar to the same dose given normally, but the slower increase in the peak concentration results in slower total drug elimination. If the antibiotic is given by a continuous infusion, it is possible to sustain the antibiotic concentration above the desired concentration target, but without the peaks and troughs that characterize the normal rapid administration. The strategy has been to give a standard dose of the antibiotic and then begin the infusion of the drug at an hourly rate that approximates the ordinary total 24-hour administration under conventional delivery methods (Fig. Some trials have indicated that distributing the infusion rate over 24 hours permits maintenance of antibiotic concentrations at target levels, but with a reduction in overall total drug that is given. Clinical trials that have compared continuous infusion to conventional drug adminis- tration are summarized in Table 3. These are time-dependent agents without an appreciable post-antibiotic effect, which makes a sustained antibiotic concentration that is above the target threshold a treatment goal (60). Reviews and meta-analysis of continuous infusion have extolled the 532 Fry Table 3 Selection of Studies where Continuous Infusion of Antibiotics Was Compared with Intermittent Infusion Patients continuous/ Authors Antibiotic(s) Type of infection intermittent Adembri et al. A prospective, randomized trial with a large population of well-stratified patients is needed to answer the question of continuous infusion of antibiotics as a superior treatment strategy. Studies have suffered from small number of patients and an absence of consistent severity in the study populations. Because the continuous infusion technique adds an additional therapeutic imposition at the bedside in the intensive care unit, additional evidence is necessary to validate the utility of this method. Prolonged Antibiotic Infusion A compromise position between conventional intermittent and continuous infusion is the concept of prolonged or extended infusion of antibiotics. As was noted in Figure 1, intermittent infusion results in a peak concentration and the peak is in part dictated by the rapidity with which the drug is infused. If the infusion is extended over three hours instead of 30 minutes, then the peak concentration will be somewhat diminished, but the rate of total drug elimination will also be delayed. Prolonged administration affords an extended period of time for the drug to have therapeutic concentrations (Fig. This extension of therapeutic concentrations has the potential for use under circumstances of adverse Vd changes in febrile, multiple-trauma patients. Studies with carbapenems (63,64) and piperacillin-tazobactam (65,66) have shown favorable pharmacokinetic profiles with prolonged infusion, but clinical evidence that compares this method with conventional antibiotic administration strategies are needed. It is clear that more clinical studies are needed and that alternative administration strategies should be explored to improve clinical outcomes. However, it is clear that antibiotic concentrations are adversely affected for most drugs as the injured and septic patient progressively accumulates “third space” volume. Clearance of antibiotics appear to be highly variable and clearly are influenced by drug concentration changes, cardiac output changes and their influence upon Antibiotic Kinetics in the Multiple-System Trauma Patient 533 kidney and liver perfusion and the intrinsic coexistent dysfunction of the kidney or liver. For most antibiotics used in the multiple-trauma patient, it is likely that they are underdosed and that inadequate antibiotic administration contributes to both treatment failures and to emerging patterns of antimicrobial resistance. More studies of antibiotic pharmacokinetics in the multiple-system injured patient are necessary. Inadequate antimicrobial prophylaxis during surgery: a study of b-lactam levels during burn debridement. Gentamicin pharmacokinetics in 1,640 patients: method for control of serum concentrations. Effect of altered volume of distribution on aminoglycoside levels in patients in surgical intensive care. Pharmacokinetic monitoring of nephrotoxic antibiotics in surgical intensive care patients. Variability in aminoglycoside pharmacokinetics in critically ill surgical patients. Aminoglycoside pharmacokinetics: dosage requirements and nephrotoxicity in trauma patients. Pharmacokinetics of vancomycin: observations in 28 patients and dosage recommendations. Stopping the use of alcohol may save a life or career but does not correct the problem buy azathioprine 50 mg on line. Even after 30 years of abstinence azathioprine 50 mg overnight delivery, I still see the beryllium present in the addiction center and the salsol, derived no doubt from endoge- nous sources, still attached to the beryllium. If any member of the family is, or was, addicted to alcohol the house should be searched for beryllium sources. The garage door to the house should be permanently closed, and the car and lawnmower kept out of it. It is not normal for them to be in the brain, they typically travel between the stomach and lungs. Their excrement dries and flies about in the dust, but mostly it resides in the soil. The eggs hatch in the stomach and the tiny larvae, microscopic in size, travel first to the lungs. Children should be treated for Ascaris anyway, whether coughing or not, once a week. Such a requirement is termed obligatory anaerobic meaning “must have absence of air. Brain abscesses and brain tumors usually have Bacteroides fra- gilis growing there. Brain tumors will not shrink unless all the parasites, bacteria and viruses are dead. Perhaps it is the toxins of the Ascaris larvae or Bacteroides or Coxsackies that induces the seizures. But by killing Ascaris, Bacteroides and Coxsackies (zapper or frequency generator at 408, 325, 364, 362. Inflammations are intended to attract calcium so a wall can be built around the intruders. Inflammations are negatively charged regions so the positively charged calcium can find its way to the inflamed site. These are found in paint (persons with seizures should never be around fresh paint) but are also found in trace amounts in carbonated beverages. A person with seizures should drink no commercial beverages: see the Recipe section for homemade carbonated and other beverages. There are several other specific brain irritants that accumulate at the seizure center. After all, seizures are an ancient malady, existing long before chemicals and solvents were manufactured. Perhaps it is these “isomers”, perhaps it is the simple overdose of a natural thing that is brain-toxic. They are often put on the boxes of cereals, rather than the cereals themselves, so the cereals can be pronounced preservative-free. Imagine how much the box must be drenched with to prevent oxygen leakage into the interior? Chickens and the eggs they lay, have lots of malvin too, stop eating chicken and eggs. Here are foods relatively free of malvin: artichokes, aspara- gus, almonds, barley, beans of all kinds, green beans, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cantaloupe, celery, nectarines, citrus, dates, 14 mango, pears, kiwi, pineapple, Granny Smith apples. Eat no whole grain products; take niacinamide 500 mg three times a day to help the liver detoxify tiny bits in other foods. Kill Ascaris, Bacteroides and Coxsackie virus and stay on a maintenance program of killing them. Keep your fingers sanitary: spray them with 10% grain al- cohol or vodka after bathroom use. Even a year after your last seizure you should carry your medicine with you and have some in your house. It might only take two days from the time of accidental swallowing of animal filth, to having little larvae in the brain. She had been completely honest with her doctor, because she was that kind of trusting person. But the social worker had called her, talked about “the law” and being an unfit mother. She planned to move, and until then would filter all the drinking water so her breast milk would be free of it too. We recommended leaving the state in order to be able to peacefully raise her child. Clara Scruggs, 50ish was losing control over her seizures and had to be hospitalized while a new medicine was tried. She was started on the herbal parasite program but could only increase by one drop of Black Walnut Hull Tincture a week, instead of daily, since each new increase would give her a seizure. After each seizure, a checkup showed she had picked up Ascaris again sometimes with additional parasites. She could not bear to put her cat outside; Boots had been a friend in need many times.
Ex- clude symptomatic individuals from food handling or care of people in hospitals order 50 mg azathioprine visa, custodial institutions and day care cen- tres; exclude asymptomatic convalescent stool-positive indi- viduals only for those with questionable handwashing habits cheap azathioprine 50mg without prescription. In communities with an adequate sewage dis- posal system, feces can be discharged directly into sewers without preliminary disinfection. Identification—A mycosis usually confined to the superficial layers of skin or mucous membranes, presenting clinically as oral thrush, intertrigo, vulvovaginitis, paronychia or onychomycosis. The single most valuable laboratory test is microscopic demonstration of pseudohyphae and/or yeast cells in infected tissue or body fluids. Culture confirmation is important, but isolation from sputum, bronchial washings, stool, urine, mucosal surfaces, skin or wounds is not proof of a causal relationship to the disease. Candida (Torulopsis) glabrata is distinguished from other causes of candidiasis by lack of pseudohyphae formation in tissue. Mode of transmission—Contact with secretions or excretions of mouth, skin, vagina and feces, from patients or carriers; by passage from mother to neonate during childbirth; and by endogenous spread. Susceptibility—The frequent isolation of Candida species from sputum, throat, feces and urine in the absence of clinical evidence of infection suggests a low level of pathogenicity or widespread immu- nity. Oral thrush is a common, usually benign condition during the first few weeks of life. Local factors contributing to superficial candidiasis include interdigital intertrigo and paronychia on hands with excessive water exposure (e. Uri- nary tract candidiasis usually arises as a complication of prolonged catheterization of the bladder or renal pelvis. Most adults and older children have a delayed dermal hypersensitivity to the fungus and possess humoral antibodies. Preventive measures: Early detection and local treatment of any infection in the mouth, oesophagus or urinary bladder of those with predisposing systemic factors (see Susceptibility) to prevent systemic spread. Fluconazole chemoprophylaxis de- creases the incidence of deep candidiasis during the first 2 months following allogenic bone marrow transplantation. Anti- fungal agents that are absorbed fully (fluconazole, ketocon- azole, itraconazole) or partially (miconazole, clotrimazole) from the gastrointestinal tract have been found to be effective in preventing oral candidiasis in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Control of patient, contacts and the immediate environment: 1) Report to local health authority: Official report not ordinarily justifiable, Class 5 (see Reporting). Topical nystatin or an azole (miconazole, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, flucon- azole) is useful in many forms of superficial candidiasis. Oral clotrimazole troches or nystatin suspension are effec- tive for treatment of oral thrush. Itraconazole suspension or fluconazole is effective in oral and oesophageal candi- diasis. Epidemic measures: Outbreaks are most frequently due to contaminated intravenous solutions and thrush in nurseries for newborns. Identification—First described in Luzon, Philippines, in the early 1960s, the disease is clinically an enteropathy with massive protein loss and a malabsorption syndrome leading to progressive weight loss and emaciation. Fatal cases are characterized by the presence of great numbers of parasites in the small intestine together with ascites and pleural transudate. Diagnosis is based on clinical findings plus the identification of eggs or larval or adult parasites in the stool. Occurrence—Intestinal capillariasis is endemic in the Philippines and in Thailand; cases have been reported from Egypt, Japan, the Republic of Korea and Taiwan (China). Isolated cases have also been reported from Colombia, India, Indonesia, and the Islamic Republic of Iran. Mode of transmission—A history of ingestion of raw or inade- quately cooked small fish eaten whole is usually obtained from patients. Experimentally, infective larvae develop in the intestines of freshwater fish that ingest eggs; monkeys, Mongolian gerbils and some birds fed these fish become infected, the parasite maturing within their intestines. Susceptibility—Susceptibility appears to be general in those geo- graphic areas in which the parasite is prevalent. Preventive measures: 1) Avoid eating uncooked fish or other aquatic animal life in known endemic areas. Control of patient, contacts and the immediate environment: 1) Report to local health authority: Case report by most practi- cable means, Class 3 (see Reporting). Epidemic measures: Prompt investigation of cases and con- tacts; treatment of cases as indicated. Identification—An uncommon and occasionally fatal disease in humans due to the presence of adult Capillaria hepatica in the liver. The picture is that of an acute or subacute hepatitis with marked eosinophilia resembling that of visceral larva migrans; the organism can disseminate to the lungs and other viscera. Diagnosis is made by demonstrating eggs or the parasite in a liver biopsy or at necropsy. Occurrence—Since identification as a human disease in 1924, about 30 cases have been reported from Africa, North and South America, Asia, Europe and the Pacific area. Reservoir—Primarily rats (as many as 86% infected in some reports) and other rodents, but also a large variety of domestic and wild mammals. Mode of transmission—The adult worms produce fertilized eggs that remain in the liver until the death of the host animal.
Azathioprine
9 of 10 - Review by M. Marus Votes: 142 votes Total customer reviews: 142 |
|