|
Download Adobe Reader
 Resize font: Resize font:
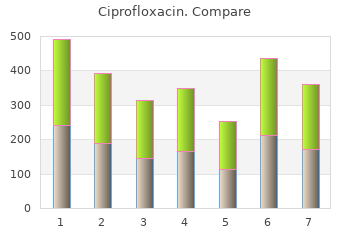
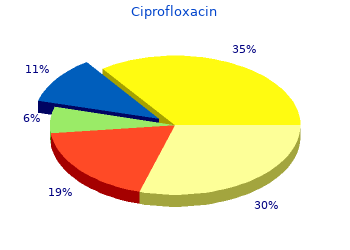
Ciprofloxacin
By Y. Kent. Lesley University. 2018. The author states: which was treated with the ischemic compression technique (see Fig generic ciprofloxacin 750 mg with amex. Ischemic and sternocleidomastoid muscles of the dominant compression technique and transverse friction side of each of 18 healthy subjects generic 250 mg ciprofloxacin overnight delivery. Corrected posture in standing required more It has been suggested that the origin of the pain muscle activity than habitual or forward head noted in fibromyalgia may also derive in large part posture in the majority of cervicobrachial and jaw from muscular ischemia (Henriksson 1999). The ratio- muscles, suggesting that a graduated approach to nale for this observation can be summarized as postural correction exercises might be required in follows: 490 Naturopathic Physical Medicine A B Figure 10. The external auditory meatus, the lateral acromion and the greater trochanter should lie along a plumb line. The external auditory meatus, the lateral acromion, the greater trochanter and the lateral malleolus should lie along a plumb line. Reproduced with permission from McLean (2005) • Morphological abnormalities have long indicated that ischemia is a feature of these muscles (Bennett 1989). Note, however, that normal muscular vascularity is seen in the non-contracting deltoideus muscle in the upper right-hand corner. Reproduced with permission from Elvin et al (2006) • The results support the suggestion that muscle Note: See the comments on hypermobility in relation ischemia contributes significantly to pain in to trigger points in Chapter 2, and in relation to pro- fibromyalgia, possibly by maintaining central lotherapy in Chapter 7, for different perspectives on sensitization/disinhibition. From previous studies, it chronic low back pain patients (Moseley et al is concluded that fear of movement (‘kinesiophobia’) 2004). A central sensitization has taken place, cognitive combination of physical (see below) and psychologi- behavioral treatment strategies (i. All patients had a posi- exercise used to diminish avoidance behavior tive outcome (Robb et al 2006). Clinical experience suggests useful alternative to the cognitive behavioral that anger can be associated with a lack of approach. Cancer patients that fluctuations in symptoms are avoided often fear a recurrence of their disease (Ahles (stabilization phase). The pacing therefore, be extremely frightening for cancer approach slowly moves towards inclusion of patients. Additional misconceptions and heightened anxiety in hydrotherapy, acupuncture and nutritional approaches many patients. The comorbidity of psychological and physical Six-week multidimensional intervention health problems in chronic illness is well documented, and it is now widely acknowledged that the manage- During the 6-week multidimensional intervention ment of chronic pain requires approaches that address (exercise, massage, relaxation, visualization and all aspects of the pain experience, such as the sensory, behavioral methods) for side-effect symptoms of affective and cognitive dimensions. Physical training of the causes of her pain; confusion over comprised three components: warm-up explanations and advice given to her. Treatment plan: Introduction of an exercise Massage could be relaxing, facilitative or regime with walking and pacing of activities therapeutic. Treatment plan: Graded exercise week focused on balance/coordination; program, including stretches and strengthening grounding and integration of the senses. During the 6-week intervention a decrease in the • Clinical finding: Altered posture secondary to scoring for 10 out of the 12 side-effects was noted pain and muscle spasm. Postural advice and correction of muscle The results of the study indicate that 6 weeks of a imbalance; advice on relaxation. As such, the total burden minutes) of pain, including myalgia, arthralgia, paraesthesia • sit-to-stand test (number of repetitions in 1 and other pain was reduced significantly minute) Patients with evidence of residual disease scored higher • arm endurance test (arm outstretched at 90° in some symptoms/side-effects compared with patients abduction and small movements, endurance in without evidence of disease. However, both groups minutes) responded positively to the intervention as indicated • range of movement: flexion and abduction of from the sum of symptoms and side-effect scores. After a 12-week intervention, significant A variety of chronic diseases are associated with pain. A repeated helpful in approaching acute systemic inflammatory measures design was used. The three treatments con- conditions, from the perspective of physical modali- sisted of ice massage, dry-towel massage and pres- ties. The role for physical treatment was evaluated sepa- The author of the research notes: rately for physical therapy and exercise programs. The theorized mechanism Casimiro et al 2002, Robinson et al 2002, Verhagen underlying ice massage is that it is a counterirritant. Ice massage may activate nerve fibers responsible for carrying the sensation of cold to the spinal cord. Although none of the outcome measures (pain, function) neuropathic pain may be exacerbated by cold, allodynia was influenced by the program (Hammond et related to postherpetic neuralgia may be decreased with al 2004). A one-time application of ice or dry- years followed a program of high-intensity towel massage may not have provided enough tactile exercise during 75-minute group sessions twice stimulation to modulate sensory input to the dorsal a week for 2 years. In the The objective of a study by Yurtkuran et al (2007) was intervention group, improvements occurred in to evaluate the effects of a yoga-based exercise muscle strength, aerobic capacity, emotional program on pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance and bio- status and quality of life. Deer had found out that Ian Weller generic 1000 mg ciprofloxacin mastercard, one of the central figures in the Concorde trials ciprofloxacin 500 mg line, working from the Middlesex Hospital and the heroic doctor whom Campbell had written about in 1988, was a Wellcome Fellow. As part of his research, Deer rang Dr Ian Weller, wanting to make last minute checks on his piece. The first was from Martin Sherwood, the public relations manager at the Wellcome Foundation. He wanted desperately to smooth over the situation, to explain everything, to put the matter in another perspective. The second phone call came in the early hours of the next morning, from Duncan Campbell. Campbell accused Deer of having threatened staff at the Academic Department of Genito-urinary Medicine at the Middlesex Hospital where Weller worked. Publicly the conflict between Campbell and Deer surfaced only in a small item in the New Statesman at the end of April. In none of these communications did Duncan Campbell present himself as a socialist in conflict with the right wing press. As far as Andrew Neil was concerned, the conflict which had been thrust upon him, and which involved a journalist renowned for his acerbic personal confrontations, was tangential to the running of a major newspaper. Deer was called in for talks and interviews, and the Sunday Times solicitors were put to work looking for a hook on which to hang an action against Campbell. The campaign which Campbell waged against Deer continued throughout 1989 and early 1990, and ended only when Deer was sent by the Sunday Times to work in America. The War on Cass Mann and Positively Healthy I will decide the route that I will follow. This was the line of enquiry which Brian Deer was to take up with his April articles in the Sunday Times. There was every sign in the first months of 1989 that Positively Healthy would grow in influence. The campaign which Duncan Campbell was planning against Cass Mann, was, however, soon to destroy all the credibility which Positively Healthy had built up. What made Positively Healthy different from many other organisations in the gay community, was the individual nature of Cass Mann and the other mainstay of the organisation, Stuart Marshall. As with all the other campaigns carried out by Campbell, there were two strands to the assault on Positively Healthy, the overt and the covert. Cass Mann and Stuart Marshall lived in a condition of fear for over a year, during the time of the campaign against them. Those who saw the public presentation of the conflict, saw only the published articles and probably concluded that there was no smoke without fire. Privately, Mann and Marshall endured a secret campaign which etched away at their confidence, their health, their self-esteem, and their social standing. It was then that 28 the real trouble began and we became targets of some unseen force. By April 1989, Duncan Campbell was expert in the techniques of covert journalistic campaigning. By circulating memoranda and letters and by telephone calls and a stream of faxes, Campbell began to get feedback from a variety of people about Cass Mann and Positively Healthy. In April 1989, a Ms Rosson of the Department of Genito-Urinary Medicine at the Withington Hospital in Manchester, sent a selection of material 30 from Positively Healthy to David Pearson. In the letter which Pearson returned to Ms Rosson, he carefully points out his qualifications for judging nutritional information. Internal evidence (sic) gives strong cause for concern that they are the latter rather than a respectable voluntary 32 organisation as you seem to believe. To this day, Cass Mann does not know how Campbell obtained the phone number of his relatives who have a different name from his family name. Right up until his death he was hurt by the allegations which were being made against his son. Throughout 1989, coincidentally with the growing conflict between Campbell and Positively Healthy, both Cass Mann and Stuart Marshall became the subjects of constant harassment from unseen forces. Both Marshall and Mann had the clear impression that their telephones were tapped. The months between April and September, the first four months of the official life of the Campaign. Against Health Fraud, Campbell spent gathering information and then privately distributing critical material against Mann, Marshall and Positively Healthy. There it came under the administrative control of the local Health Authority and was answerable within the hospital to the senior medical consultant.
In the following discount 750 mg ciprofloxacin with amex, Finally discount ciprofloxacin 1000mg, new developments in non-invasive the most important mediators of infarct progression molecular imaging are of increasing interest for will be discussed. These methods make use of contrast probes that trace gene transcription or of Brain infarcts grow in three phases: intracellular conjugates that reflect the metabolic acute phase, within a few minutes after the onset status and/or bind to stroke markers. The number of ischemia; terminal depolarization of cell of molecules that can be identified by these methods membranes; rapidly expands and greatly facilitates the regional subacute phase, within 4–6 hours; molecular analysis of stroke injury. Progression of ischemic injury With the advent of non-invasive imaging evidence has Peri-infarct spreading depression been provided that brain infarcts grow. This growth is A functional disturbance contributing to the growth not due to the progression of ischemia because the of the infarct core into the penumbra zone is activation of collateral blood supply and spontaneous the generation of peri-infarct spreading depression- thrombolysis tend to improve blood flow over time. These depolarizations are Infarct progression can be differentiated into three initiated at the border of the infarct core and spread phases. During the acute phase tissue injury is the over the entire ipsilateral hemisphere. During spread- direct consequence of the ischemia-induced energy ing depression the metabolic rate of the tissue mark- failure and the resulting terminal depolarization of edly increases in response to the greatly enhanced cell membranes. At flow values below the threshold energy demands of the activated ion-exchange of energy metabolism this injury is established within pumps. In the healthy brain the associated increase a few minutes after the onset of ischemia. During the of glucose and oxygen demands is coupled to a paral- subsequent subacute phase, the infarct core expands lel increase of blood flow but in the peri-infarct into the peri-infarct penumbra until, after 4–6 hours, penumbra this flow response is suppressed or even core and penumbra merge. As a result, a misrelationship arises expansion are peri-infarct spreading depressions and between the increased metabolic workload and the low a multitude of cell biological disturbances, collectively oxygen supply, leading to transient episodes of hypoxia referred to as molecular cell injury. Finally, a delayed and the stepwise increase in lactate during the passage phase of injury evolves which may last for several of each depolarization. During this phase secondary The pathogenic importance of peri-infarct depo- phenomena such as vasogenic edema, inflammation larizations for the progression of ischemic injury is and possibly programmed cell death may contribute supported by the linear relationship between to a further progression of injury. The largest increment of infarct volume occurs Correlation analysis of this relationship suggests that during the subacute phase in which the infarct core during the initial 3 hours of vascular occlusion each expands into the penumbra. Using multiparametric depolarization increases the infarct volume by more imaging techniques for the differentiation between than 20%. This is probably one of the reasons that core and penumbra, evidence could be provided that glutamate antagonists reduce the volume of brain 1 hour after occlusion of the middle cerebral artery infarcts because these drugs are potent inhibitors of 15 the penumbra is still approximately of the same size spreading depression. Section 1: Etiology, pathophysiology and imaging Peri-infarct spreading depressions are depolariza- pathogenic importance in different ischemia models. Therefore, the relative contribution of the following injury mechanisms differs in different types Molecular mechanisms of injury of ischemia. As the severity of acidosis correlates with the “molecular” does not anticipate any particular injury severity of ischemic injury, it has been postulated that pathway (Figure 1. Schematic representation of molecular injury pathways leading to mitochondrial failure and the endoplasmic reticulum 16 stress response. Injury pathways can be blocked at numerous sites, providing multiple approaches for the amelioration of both necrotic and apoptotic tissue injury. The changes in suggests that acidosis may induce calcium toxicity, intracellular calcium activity are highly pathogenic: and that this effect is the actual mechanism of acido- prolonged elevation of cytosolic calcium causes mito- toxicity [68]. The activation of ionotropic glutamate secondary disturbances, notably inhibition of protein receptors results in the inflow of calcium from the synthesis. Calcium-dependent pathological events are extracellular into the intracellular compartment, therefore complex and contribute to a multitude of leading to mitochondrial calcium overload and the secondary molecular injury pathways. However, following quences of free radical reactions are the release pharmacological inhibition of ionotropic glutamate of biologically active free fatty acids such as arachi- receptors, an apoptotic injury mechanism evolves donic acid, the induction of endoplasmic reticulum that may prevail under certain pathophysiological stress, the induction of mitochondrial disturbances conditions. The latter may induce ischemic cell injury has been debated, but this does apoptosis and thus enhance molecular injury not invalidate the beneficial effect of glutamate pathways related to mitochondrial dysfunction. An The therapeutic benefit of free radical scavengers, explanation for this discrepancy is the above- however, is limited, as recently documented by the described pathogenic role of peri-infarct depolariza- therapeutic failure of the free-radical-trapping agent tions in infarct expansion. During ischemia anoxic depolarization in com- flow and the alleviation of hypoxic injury, whereas bination with the activation of ionotropic glutamate in neurons it contributes to glutamate excitotoxicity and acid-sensing ion channels causes a sharp rise of and – by formation of peroxynitrate – to free-radical- cytosolic calcium [70]. However, zinc may also exhibit neuro- ally will cause disruption of the outer mitochondrial protective properties, indicating that cells may possess membrane and the release of pro-apoptotic mito- a specific zinc set-point by which too little or too chondrial proteins (see below). It is initiated A large number of biochemical substrates, molecules and mechanisms are involved in the by the ischemia-induced release of calcium stores progression of ischemic damage. This again leads to selective inhib- tigated in the search for possible pharmacological ition of polypeptidepol chain initiation, disaggregation targets (for review see Rothwell and Luheshi [79]). Infarct reduction was also observed after components of the translation complex [77]. The increase in permeability 18 of the inner mitochondrial membrane has two Inflammatory reactions are important modulators pathophysiologically important consequences.
The Macklin effect: a fre- The shuttle (6 min) walk distance was not predictive of a poor quent etiology for pneumomediastinum in severe blunt surgical outcome ciprofloxacin 250 mg cheap. Chest 2002; 121:1269–1277 dysfunction after cardiac operations: electrophysiologic This article reviews the associated physiologic generic ciprofloxacin 750mg line, biochemical, evaluation of risk factors. Perioperative predictors of extubation associated with this complication by logistic regression analy- failure and the effect on clinical outcome after cardiac sis was the use of cardioplegic ice slush. Postoperative pulmonary dysfunction resulting in failure to wean from mechanical ventilator in adults after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary support after coronary artery bypass surgery. Med 1990; 18:499–501 Am J Crit Care 2004; 13:384–393 Report of four patients who had diaphragmatic flutter after A nursing review that is worth reading with 159 references. Symptomatic persistent necrosis factor gene polymorphisms and prolonged postcoronary artery bypass graft pleural effusions mechanical ventilation after coronary artery bypass requiring operative treatment: clinical and histologic surgery. Clinical relevance of The effusions were lymphocytic ( 80% lymphocytes) and often angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphisms to resulted in fibrosis and occasional trapped lungs. Thorax 1990; 45:465–468 922–927 Thoracic wall discoordination was documented by magnetom- The presence of a specific haplotype in the promoter region of eters in 9 of 16 patients 1 week postoperatively. Key words: circadian rhythm; polysomnography; sleep; sleep deprivation; sleep homeostasis; sleep physiology Sleep-Wake Regulation Two basic intrinsic components interact to regulate the timing and consolidation of sleep and Sleep is a complex reversible state characterized wake: sleep homeostasis, which is dependent on by both behavioral quiescence and diminished the sleep-wake cycle, and circadian rhythm, which responsiveness to external stimuli. Neuroscience of Sleep Sleep homeostasis is defined as increasing sleep pressure related to the duration of previous Neural systems generating wakefulness wakefulness: the longer a person is awake, the include the ascending reticular formation in the sleepier one becomes. In con- (wake-maintenance zones), namely in the late trast, only metabolic control is present during morning and early evening; there are also two sleep. Compared with levels during wakefulness, circadian troughs in alertness (increased sleep there is a decrease in both Pao and arterial oxygen 2 propensity) in the early morning and early saturation (Sao ) and an increase in Paco during 2 2 midafternoon. Retinal photoreceptors are most acterized by periodic breathing, with episodes of sensitive to shorter-wavelength light (450 to 500 hypopnea and hyperpnea. Nocturnal sleep typically occurs dur- of others decrease during sleep (eg, cortisol, insulin, ing the decreasing phase of the temperature and thyroid-stimulating hormone). Several physiologic parameters become increased during sleep deprivation, including subjective and objective sleepiness, sympathetic Musculoskeletal System activity, insulin resistance, and levels of cortisol and ghrelin. Two patterns of eye move- current and direct current amplifiers and filters that ments can often be seen: slow rolling eye move- are used to record physiologic variables during ments that occur during drowsiness when eyes are sleep. Derivation consists voltage between two electrodes and can either be of one electrode below and one electrode above the bipolar, ie, when two standard electrodes are mandible. With nasal air pressure of the brain (F [frontal], C [central], O [occipital], monitoring, inspiratory flow signals show a pla- and M [mastoid]), and a numerical subscript, with teau (flattening) with obstructive events or reduced odd numbers representing left-sided electrodes, but rounded signal with central events. Event precedes an Polysomnographic features of many primary arousal, and does not meet criteria for either sleep, medical, neurologic and psychiatric disor- apneas or hypopneas. Smoking is not allowed medications, whereas the low sleep input pattern prior to each nap trial, and persons should not often accompanies disorders presenting with drink caffeine or engage in vigorous physical insomnia or use of stimulant medications. Epworth Sleepiness Scale The multiple sleep latency test consists of 4 or 5 nap opportunities performed every 2 h, The degree of sleepiness is often subjectively with each nap trial lasting 20 min in duration. Sleep onset latency out a break, (e) lying down to rest in the afternoon, is recorded as 20 min if no sleep occurs during (f) sitting and talking to someone, (g) sitting quietly a nap trial. Each nap trial is terminated after 20 after lunch without drinking alcohol, and min if no sleep is recorded; if sleep is noted, the (h) stopped in a car for a few minutes in traffic. Practice parameters disorders, including dementia and Parkinson for clinical use of the multiple sleep latency test disease; psychiatric disorders, such as depression; and the maintenance of wakefulness test. Air- despite the presence of respiratory efforts caused way size is also influenced by lung volume, which by partial or complete upper-airway occlusion 1 decreases during sleep. Complex sleep apnea is characterized by sites of upper-airway obstruction are behind the central apneas that develop or become more palate (retropalatal), behind the tongue (retrolin- frequent during continuous positive airway gual), or both. Hormone- ory); erectile dysfunction; gastroesophageal reflux; replacement therapy has been suggested for post- nocturia; driving and work-related accidents; menopausal women; however, data regarding its impaired school and work performance; and efficacy for this indication are inconsistent. Finally, noninva- as the result of aerophagia; or chest discomfort and sive positive pressure ventilation is indicated for tightness, many of which may result in the patient cases of persistent sleep-related hypoventilation discontinuing therapy. Factors oral devices; and tongue-retaining devices which, predicting the need for heated humidification by securing the tongue in a soft bulb located ante- include the following: (1) age 60 years, (2) use of rior to the teeth, hold the tongue in an anterior drying medications, (3) presence of chronic muco- position. In addition, mandibular reposi- should be considered whenever there is doubt tioners should not be used in persons with inad- about a person’s degree of sleepiness. Nasal septo- resistance accompanied by increased or constant plasty, polyp removal, and turbinectomy are used respiratory effort and arousals from sleep. Uvulopalatopharyngoglossoplasty and arousals and are followed by less negative esoph- maxillomandibular advancement increase the ret- ageal pressure excursions as airflow increases rolingual, retropalatal, and transpalatal airway. Nasal pressure monitoring dem- Finally, tracheotomy can be used to bypass the onstrates inspiratory flattening followed by a narrow upper airway and is the only surgical pro- rounded contour during arousals. Practice hypoventilation developing during sleep, includ- parameters for the use of autotitrating continuous ing a decrease in minute ventilation and/or tidal positive airway pressure devices for titrating pres- volume, abnormal ventilation/perfusion relation- sures and treating adult patients with obstructive ships, or changes in ventilatory chemosensitivity sleep apnea syndrome: An update for 2007. Key words: circadian rhythm sleep disorders; insomnia; nar- colepsy; parasomnias; restless legs syndrome; sleepiness Insomnia Insomnia is characterized by repeated difficulty with either falling or staying asleep that is associ- The differential diagnoses of excessive sleepiness 1 ated with impairment of daytime function. Persons with insomnia have an increased risk Likewise, there is no daytime napping or impair- of psychiatric illness developing, such as major ment of daytime functioning. Ciprofloxacin
8 of 10 - Review by Y. Kent Votes: 230 votes Total customer reviews: 230 |
|